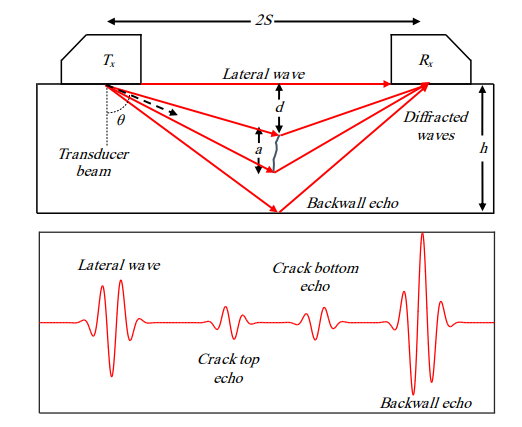
TOFD – Time of Flight Diffraction
TOFD is different from other UT methods is a sense that, rather than measuring only the high amplitude sound waves that reflects off of the back of the component, it instead measures the response time of low amplitude waves that are diffracted by the tips of cracks.
TOFD uses a separate emitter and receiver, that are held in a fixed geometry, as they are scanned along a surface of a test sample. A pulse of ultrasound is generated at each scan position (an A-Scan), ultrasonic waves propagate into the bulk of the sample, scatter off any defects present, and are subsequently received, before moving to the next scan position. Diffraction causes energy to be spread over a wide angular range; TOFD aims to detect weak diffracted waves arising at edges and tips, which can be used to size defects accurately, whilst avoiding stronger specular reflections which often mask them.